什么是 Web Server
Web Service是一个平台独立的,低耦合的,自包含的、基于可编程的web的应用程序,可使用开放的XML(标准通用标记语言下的一个子集)标准来描述、发布、发现、协调和配置这些应用程序,用于开发分布式的交互操作的应用程序。
关于 HTTP
超文本传输协议(HTTP)的设计目的是保证客户机与服务器之间的通信。HTTP 的工作方式是客户机与服务器之间的请求-应答协议。
HTTP是基于客户 / 服务器模式,且面向连接的。典型的HTTP事务处理有如下的过程
- 客户与服务器建立连接
- 客户向服务器提出请求
- 服务器接受请求,并根据请求返回相应的文件作为应答
- 客户与服务器关闭连接
构成部分
Request

Request Line
1
| Request Line = Method SP Request-URI SP HTTP-Version CRLF
|
Method
1
| GET、PUT、POST、DELETE、CONNECT、OPTIONS、TRACE、PATCH
|
SP
分隔符,ASCII码中的空格。
Request-URI
1
| Request-URI = "*" | absoluteURI | abs_path | authority
|
实际传输的时候 Request-URI 有两种可能的形式,一种是完整的 absoluteURI,包含Schema和Host,另一种是abs_path,并没有包含Schema(http)和Host(mrpeak.cn)部分,Host部分被移交到了Header当中。所以平时我们抓包,有时看到的是完整的URI,有时则只有路径信息。
HTTP-Version
代表我们当前使用的版本。
CRLF
由两个字节组成。CR值为16进制的0x0D,对应ASCII中的回车键,LF值为0x0A,对应ASCII中的换行键,CRLF合起来就是我们平常所说的\r\n。
Header 本质上是一些文本键值对
Body
请求体
Response
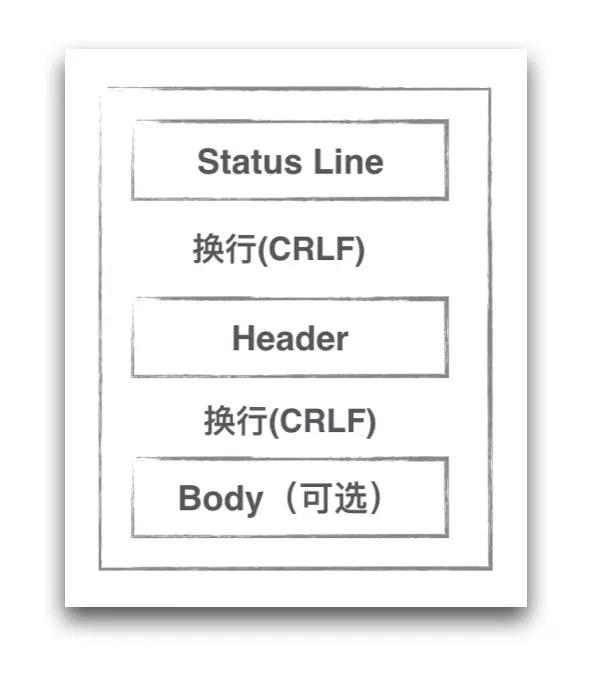
Status Line
1
| Status-Line = HTTP-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF
|
Body
Node.JS 对于 HTTP 的实现
Request
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| class IncomingMessage extends stream.Readable {
constructor(socket: Socket);
aborted: boolean;
httpVersion: string;
httpVersionMajor: number;
httpVersionMinor: number;
complete: boolean;
/**
* @deprecate Use `socket` instead.
*/
connection: Socket;
socket: Socket;
headers: IncomingHttpHeaders;
rawHeaders: string[];
trailers: NodeJS.Dict<string>;
rawTrailers: string[];
setTimeout(msecs: number, callback?: () => void): this;
/**
* Only valid for request obtained from http.Server.
*/
method?: string;
/**
* Only valid for request obtained from http.Server.
*/
url?: string;
/**
* Only valid for response obtained from http.ClientRequest.
*/
statusCode?: number;
/**
* Only valid for response obtained from http.ClientRequest.
*/
statusMessage?: string;
destroy(error?: Error): void;
}
|
Response
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class ServerResponse extends OutgoingMessage {
statusCode: number;
statusMessage: string;
constructor(req: IncomingMessage);
assignSocket(socket: Socket): void;
detachSocket(socket: Socket): void;
// https://github.com/nodejs/node/blob/master/test/parallel/test-http-write-callbacks.js#L53
// no args in writeContinue callback
writeContinue(callback?: () => void): void;
writeHead(statusCode: number, reasonPhrase?: string, headers?: OutgoingHttpHeaders): this;
writeHead(statusCode: number, headers?: OutgoingHttpHeaders): this;
writeProcessing(): void;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class OutgoingMessage extends stream.Writable {
upgrading: boolean;
chunkedEncoding: boolean;
shouldKeepAlive: boolean;
useChunkedEncodingByDefault: boolean;
sendDate: boolean;
finished: boolean;
headersSent: boolean;
connection: Socket;
socket: Socket;
constructor();
setTimeout(msecs: number, callback?: () => void): this;
setHeader(name: string, value: number | string | string[]): void;
getHeader(name: string): number | string | string[] | undefined;
getHeaders(): OutgoingHttpHeaders;
getHeaderNames(): string[];
hasHeader(name: string): boolean;
removeHeader(name: string): void;
addTrailers(headers: OutgoingHttpHeaders | Array<[string, string]>): void;
flushHeaders(): void;
}
|
Express
1
| Fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for node.
|
Express 框架建立在内置模块 HTTP 之上
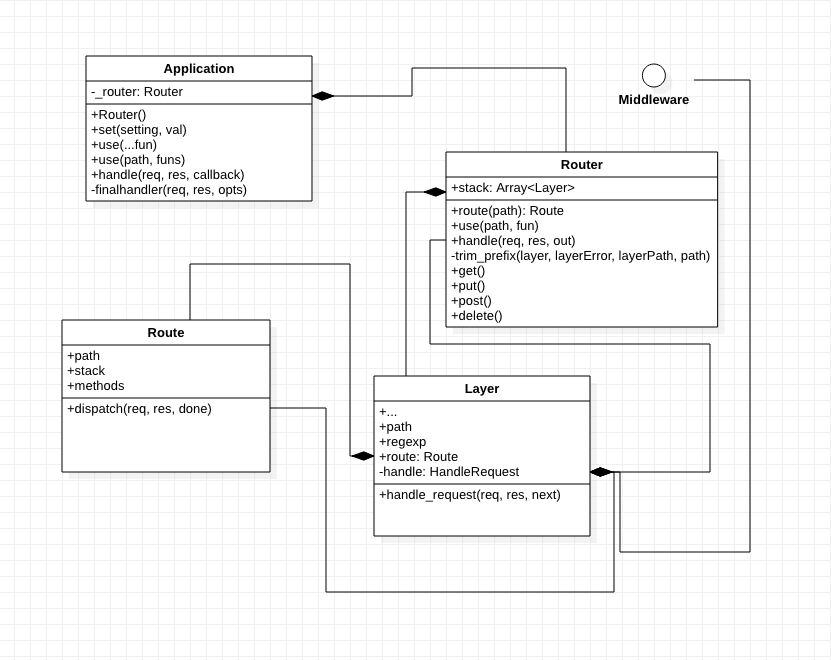
Application
在 Express 项目初始化完成后,本质是一个 RequestListener,接收来自于 HTTP 模块的 Request、Response 两个参数。
主要方法
Router
作为整个 WEB 应用的路由调度层,负责初始化时创建接口及运行时的接口、中间件、子 Router 匹配。
主要方法
Application.use 的依赖方法,实现套娃的主要方法
路由、中间件的匹配调度
生成 Route 实例,具体的接口
Layer
每一个Route、Middleware、Route 都是由 Layer 进行包装
主要方法
分发调度路由、中间件、接口
Route
具体接口的实例
拜~





